Polyols are a diverse group of compounds that play a crucial role in various industries, thanks to their unique properties and applications. These versatile chemicals are characterized by the presence of multiple hydroxyl (-OH) groups, which can vary in number and arrangement. In this in-depth SEO article, we will explore polyols, with a specific focus on the significance of their different molecular weights and their extensive use in various industries.
Understanding Polyols
Polyols, also known as polyhydric alcohols, are a class of organic compounds that contain multiple hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups. These hydroxyl groups make polyols highly reactive and give them unique chemical and physical properties. Polyols can be derived from both natural and synthetic sources and are used in a wide range of applications due to their versatility.
Polyols with different molecular weight
Low Molecular Weight Polyols
Low molecular weight polyols typically contain 2 to 5 hydroxyl groups. They are smaller in size and are often derived from natural sources like sugars and starch. These polyols are known for their solubility, low viscosity, and low volatility. They find applications in various industries.
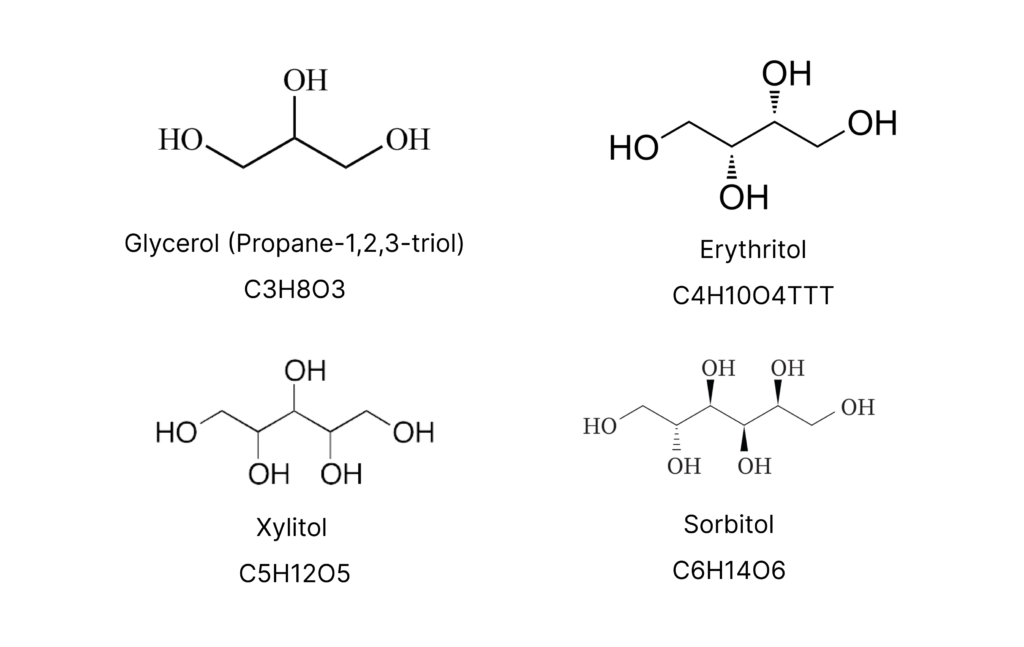
Glycerol (Propane-1,2,3-triol)
Glycerol, chemically known as Propane-1,2,3-triol, is a versatile and indispensable organic compound characterized by its unique trihydroxy structure. This colorless, odorless liquid plays a pivotal role in various industries, owing to its exceptional properties as a humectant, solvent, and sweetening agent.
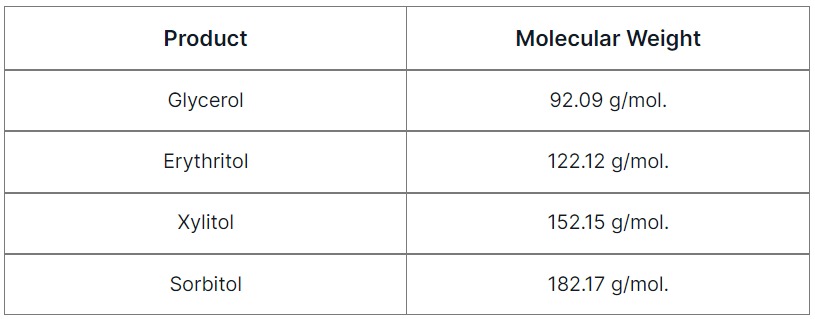
Product
Molecular Weight
Glycerol
92.09 g/mol.
Erythritol
122.12 g/mol.
Xylitol
152.15 g/mol.
Sorbitol
182.17 g/mol.
Scroll
Uses of Glycerol
Moisturising Agent
Glycerol is a key component in skincare products, as it attracts and retains moisture, keeping the skin hydrated and preventing dryness.
Food and Beverage
It serves as a humectant in food products, preventing them from drying out, and is used in the production of sweeteners and syrups.
Pharmaceuticals
Glycerol is used as a solvent for drugs and as an excipient in various pharmaceutical formulations.
Explosives
It plays a critical role in the production of explosives like nitroglycerin due to its nitrate groups.
Erythritol
Erythritol, a natural sugar alcohol, is gaining popularity as a low-calorie sweetener and sugar substitute. Known for its remarkable sweetness without the caloric impact of sugar, erythritol is derived from natural sources and is a favorite among those seeking healthier alternatives in food and beverages.
Uses of Erythritol
Sugar Substitute
Erythritol is used as a low-calorie sugar substitute in a variety of sugar-free and diet products.
Dental Care
It inhibits dental cavities and is added to chewing gums, mints, and toothpaste to promote oral health.
Pharmaceuticals
Erythritol is used as a filler in tablets and capsules, providing bulk to pharmaceutical formulations.
Baking and Confectionery
It is used in sugar-free baking and confectionery as a sweetening agent without the added calories.
Xylitol
Xylitol is a naturally occurring sugar alcohol known for its sweet taste and remarkable dental benefits. Derived from various natural sources, such as birch bark and corncobs, xylitol is a popular sugar substitute in sugar-free gum, candies, and dental care products.
Uses of Xylitol
Dental Health
Xylitol inhibits the growth of cavity-causing bacteria, making it a common ingredient in oral care products like toothpaste, mouthwash, and chewing gum.
Sugar-Free Products
Xylitol is used to sweeten sugar-free gum, candies, and diabetic-friendly foods.
Otolaryngology
It is employed as a nasal spray to reduce the risk of ear infections.
Medicinal Syrups
Xylitol is added to cough syrups and liquid medications to improve taste and palatability.
Sorbitol
Sorbitol, a sugar alcohol derived from fruits and berries, is a versatile and low-calorie sweetener that finds extensive use in food, pharmaceuticals, and personal care products. Its unique humectant properties make it a valuable ingredient in skincare, haircare, and oral care formulations, helping to retain moisture and promote product stability.
Uses of Sorbitol
Sugar Substitute
Sorbitol is used in sugar-free and reduced-calorie food products, including sugar-free candies and desserts.
Pharmaceutical Applications
It is utilized as a sweetening agent and as a filler in medicinal syrups and tablets.
Oral Care
Sorbitol can be found in toothpaste, mouthwash, and sugar-free gum to help prevent tooth decay.
Cosmetics and Personal Care
Sorbitol’s humectant properties make it a common ingredient in skincare and haircare products, helping to retain moisture.
Medium Molecular Weight Polyols
Medium molecular weight polyols contain 6 to 10 hydroxyl groups and are often used as building blocks for more complex polymers and resins. These polyols offer a balance between reactivity and viscosity, making them suitable for applications.
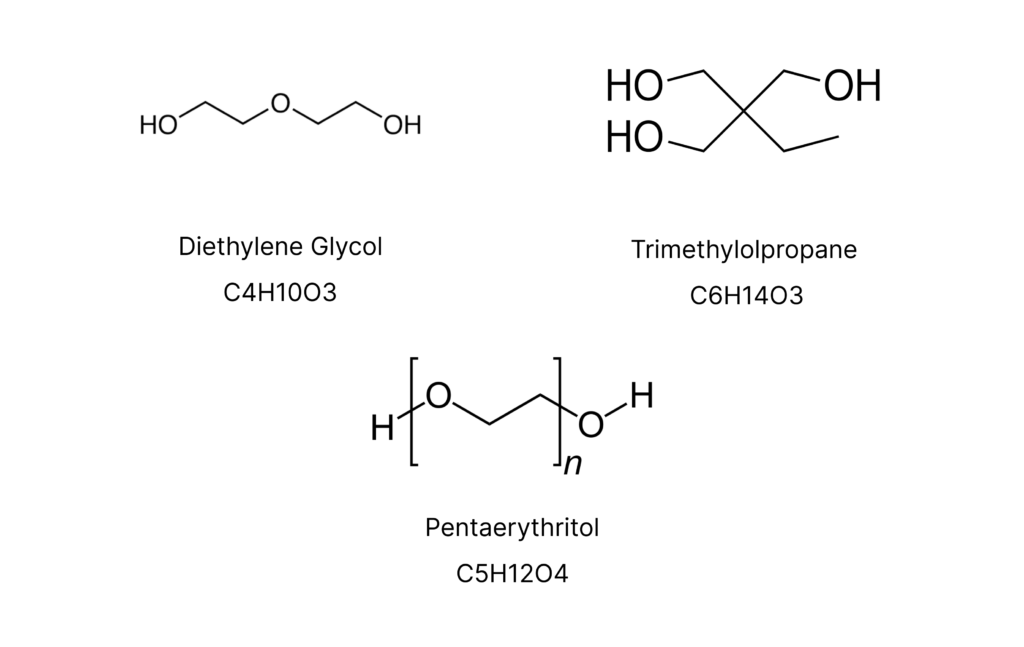
Diethylene Glycol
Diethylene Glycol is a clear, colorless liquid with a slightly sweet taste, primarily known for its role in industrial applications. It serves as an efficient coolant and heat transfer fluid, used in various industrial processes. Additionally, diethylene glycol finds use as a solvent for dyes, inks, and various chemical formulations, as well as an ingredient in deicing solutions and antifreeze, making it a versatile compound in multiple industrial sectors.
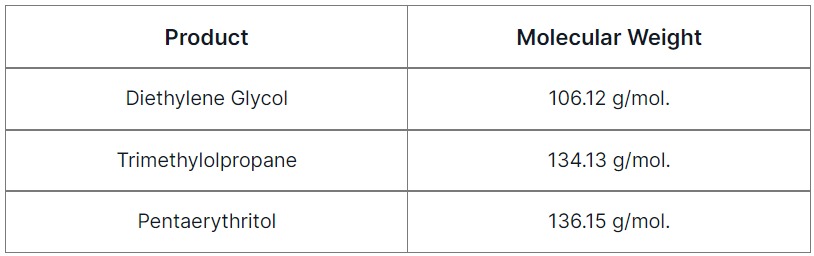
Product
Molecular Weight
Diethylene Glycol
106.12 g/mol.
Trimethylolpropane
134.13 g/mol.
Pentaerythritol
136.15 g/mol.
Scroll
Uses of Diethylene Glycol
Coolant and Heat Transfer Fluid
Diethylene glycol is used as an efficient coolant and heat transfer fluid in various industrial processes and systems.
Solvent
It serves as a solvent for dyes, inks, and various chemical formulations, including brake fluids and hydraulic fluids.
Deicing and Antifreeze
Diethylene glycol is an ingredient in deicing solutions and antifreeze formulations for both automobiles and aircraft.
Pharmaceuticals
It is used in some pharmaceutical formulations and cough syrups as a solvent.
Trimethylolpropane
Trimethylolpropane, often abbreviated as TMP, is a versatile organic compound renowned for its significant role in the production of high-performance materials. With its tri-functional hydroxyl groups, TMP is a crucial building block for polyurethanes, alkyd resins, and other advanced polymers.
Uses of Trimethylolpropane
Polyurethane Production
Trimethylolpropane is a key component in the production of polyurethane coatings, adhesives, and foams, contributing to their durability and resilience.
Alkyd Resins
It is used to make alkyd resins for paints and coatings, providing excellent weather resistance and gloss retention.
Fuel Additives
Trimethylolpropane is employed as a fuel additive to improve combustion and reduce emissions.
Plasticizers
It is used as a plasticizer to enhance the flexibility and durability of various plastic products.
Pentaerythritol
Pentaerythritol, a versatile polyhydric alcohol, is a key ingredient in the production of high-performance materials and specialty chemicals. Known for its multifunctional hydroxyl groups, pentaerythritol is widely employed in the formulation of alkyd resins, explosives, and fire-retardant coatings.
Uses of Pentaerythritol
Alkyd Resins
Pentaerythritol is a key component in alkyd resin formulations, widely used in the production of paints and coatings with excellent adhesion and durability.
Explosives
It is utilized in the manufacture of explosive materials due to its high energy content.
Plastic Stabilizers
Pentaerythritol is used in fire-retardant coatings for various applications, including construction and textiles.
Fire Retardants
Pentaerythritol is used in fire-retardant coatings for various applications, including construction and textiles.
High Molecular Weight Polyols
High molecular weight polyols contain more than 10 hydroxyl groups and are typically large and complex molecules. These polyols have higher viscosity and are valued for their enhanced reactivity, making them suitable for advanced applications.
Polyethylene Glycol (PEG): PEGs come in various molecular weights, and the number in parentheses indicates the average molecular weight. For example:
PEG 400 (Molecular Weight: 400 g/mol)
PEG 1000 (Molecular Weight: 1000 g/mol)
PEG 4000 (Molecular Weight: 4000 g/mol)
PEG 400 (Molecular Weight: 400 g/mol)
PEG 1000 (Molecular Weight: 1000 g/mol)
PEG 4000 (Molecular Weight: 4000 g/mol)
Polyester Polyols: The molecular weight of polyester polyols can vary significantly based on the specific formulation, but they are generally in the range of several thousand g/mol or higher.
Polycaprolactone (PCL): The molecular weight of PCL typically ranges from 530 g/mol to 80,000 g/mol or even higher, depending on the intended use.
Polytetrahydrofuran (PolyTHF): PolyTHF can have molecular weights ranging from around 650 g/mol to 3,000 g/mol, depending on the desired properties and application.
Polybutadiene Polyols: The molecular weight of polybutadiene polyols can vary widely, but they are typically in the range of several thousand g/mol to tens of thousands of g/mol, depending on the specific formulation.
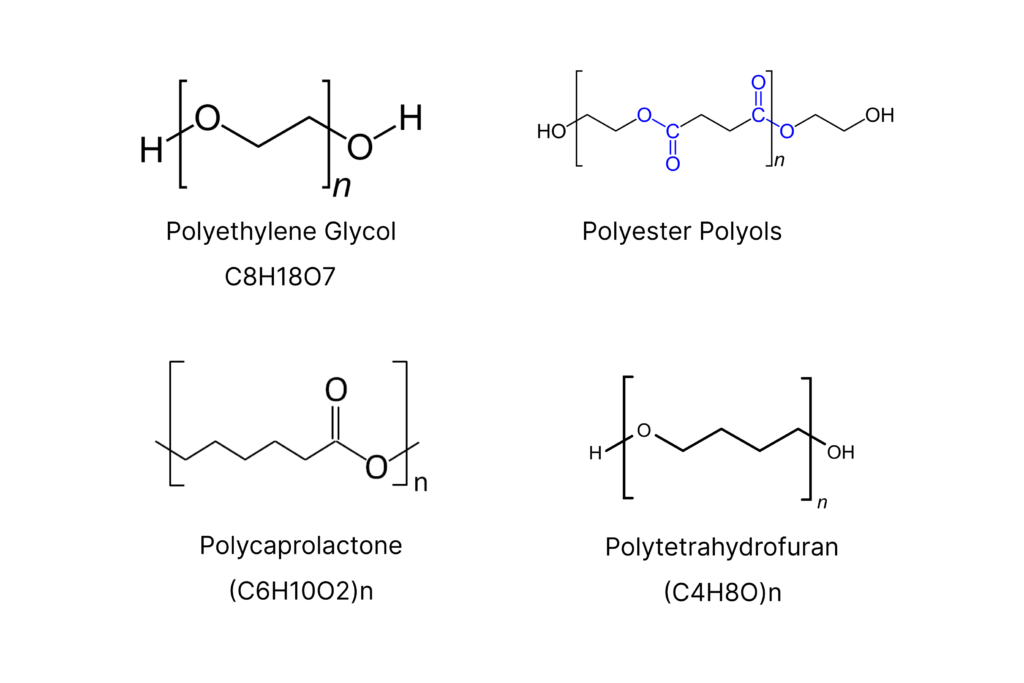
Products
Range
Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)
400 g/mol) to 4000 g/mol
Polyester Polyols
several thousand g/mol or higher.
Polycaprolactone (PCL)
530 g/mol to 80,000 g/mol
Polytetrahydrofuran (PolyTHF)
650 g/mol to 3,000 g/mol
Polybutadiene Polyols
several thousand g/mol to tens of thousands of g/mol
Scroll
Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)
Polyethylene Glycol, commonly referred to as PEG, is a versatile polymer known for its wide-ranging applications. With variable molecular weights, PEG is used in pharmaceuticals as a solubilizing agent and as a base for various drug formulations. It plays a crucial role in cosmetics, providing moisture and texture to skincare products, and is used as a food additive, food packaging, and in industrial processes.
Uses of Polyethylene Glycol(PEG)
Pharmaceuticals
PEG is used in drug formulations as a solubilizing and stabilizing agent, especially for poorly water-soluble drugs.
Food and Beverage
PEGs are used as food additives and in the manufacturing of food packaging to improve food preservation.
Lubricants and Industrial Fluids
PEGs serve as a lubricant and hydraulic fluid in various industrial applications.
Polymer Processing
PEGs are used in the plastics and polymer industries as processing aids and mould release agents.
Polyester Polyols
Polyester Polyols are a class of high-performance compounds essential in the creation of durable and versatile materials. These polyols, used as building blocks for various
polymers, are prominently featured in the production of resilient paints and coatings, fiberglass-reinforced plastics, and high-quality adhesives.
Uses of Polyester Polyols
Paints and Coatings
Polyester polyols are integral in the production of high-performance paints and coatings with exceptional adhesion and resistance properties.
Fiberglass Reinforced Plastics
They are used in the production of composites and fibreglass-reinforced plastics for the automotive, marine, and construction industries.
Adhesives and Sealants
Polyester polyols enhance the properties of adhesives and sealants used in construction and aerospace applications.
Polyurethane Foams
They are a key component in the creation of rigid and flexible polyurethane foams for insulation and cushioning.
Polycaprolactone (PCL)
Polycaprolactone, often abbreviated as PCL, is a biodegradable and highly versatile polymer known for its unique properties. With a low melting point and excellent biocompatibility, PCL is extensively used in 3D printing, medical devices, and drug delivery systems.
Uses of Polycaprolactone(PCL)
3D Printing
PCL is used in 3D printing due to its biocompatibility, low melting point, and easy processability.
Biodegradable Materials
It is used to create biodegradable products, such as surgical sutures, drug delivery systems, and wound dressings.
Orthopaedic Implants
PCL-based materials are used in the development of orthopedic implants like bone plates and screws.
Adhesives and Sealants
PCL is employed in adhesives and sealants for its flexibility and adhesion properties.
Polytetrahydrofuran (PolyTHF)
Polytetrahydrofuran, commonly referred to as PolyTHF, is a polymer with a remarkable blend of properties that make it invaluable in various industrial applications. Known for its excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility, PolyTHF is a key ingredient in elastomers, spandex fibers, and thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPU).
Uses of Polytetrahydrofuran (PolyTHF)
Elastomers
PolyTHF is used in the production of elastomers, providing flexibility, durability, and resistance to abrasion and chemicals.
Spandex Fibres
It is a key component in the production of spandex fibers, giving them their stretch and recovery properties.
Coatings
It serves as a resin in high-performance coatings, offering excellent weather resistance and durability.
Thermoplastic Polyurethanes (TPU)
PolyTHF is used in TPU production for applications like footwear, tubing, and automotive components.
Polybutadiene Polyols
Polybutadiene Polyols are a family of high-performance polymers with unique attributes that enhance a wide range of products. Known for their strength and flexibility, these polyols are vital in the production of specialized polyurethane foams, adhesives, and composites.
Uses of Polybutadiene Polyols
Polyurethane Foams
Polybutadiene polyols are used in the production of specialty polyurethane foams with enhanced mechanical properties for applications such as cushioning and insulation.
Automotive and Aerospace Composites
They are employed in the development of lightweight, high-strength composites for automotive and aerospace components.
Adhesives and Sealants
Used as binders and modifiers in adhesives and sealants to improve their performance.
Construction Materials
Polybutadiene polyols are used in the formulation of high-strength, fast-curing concrete for construction applications.
Contact Us
Questions or looking for a quote?




